I Do, and I Understand — How Does XR Empower Experiential Learning?
)
I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand. Confucius.
Experiential learning remains a cornerstone of immersive training and a key advantage of using virtual, augmented, and mixed reality (VR/AR/MR) solutions. With these theoretical techniques, institutions, companies and organisations can rapidly upskill and onboard new hires, reskill employees and prepare the workforce for the future.
Studies show that technologies like extended reality (XR) can improve learner retention by 75 percent. It is possible to train individuals four times faster and build greater confidence compared to traditional reading and lecture-based instruction.
So why does experiential learning and XR go hand in hand? Mixed reality industry news, XR Today, takes a closer look.
David Kolb and Experiential Training
Experiential learning has been shown in countless global studies around the world to be a key aspect of holistic teaching methods. This is the practice in which direct experiences engage learners at the practical and sensory level to enhance cognitive learning at rates multiple times that of traditional instruction.
With it, instructors recognise that deep learning trumps surface-level learning by pragmatic, hands-on experience. Learners can complete tasks through several different methodologies, including discussions, rehearsals and role-playing.
US Educational Theorist David Kolb, a progenitor of such theories, has developed his practices throughout the 80s and written extensively on the subject. This is his four-stage approach.
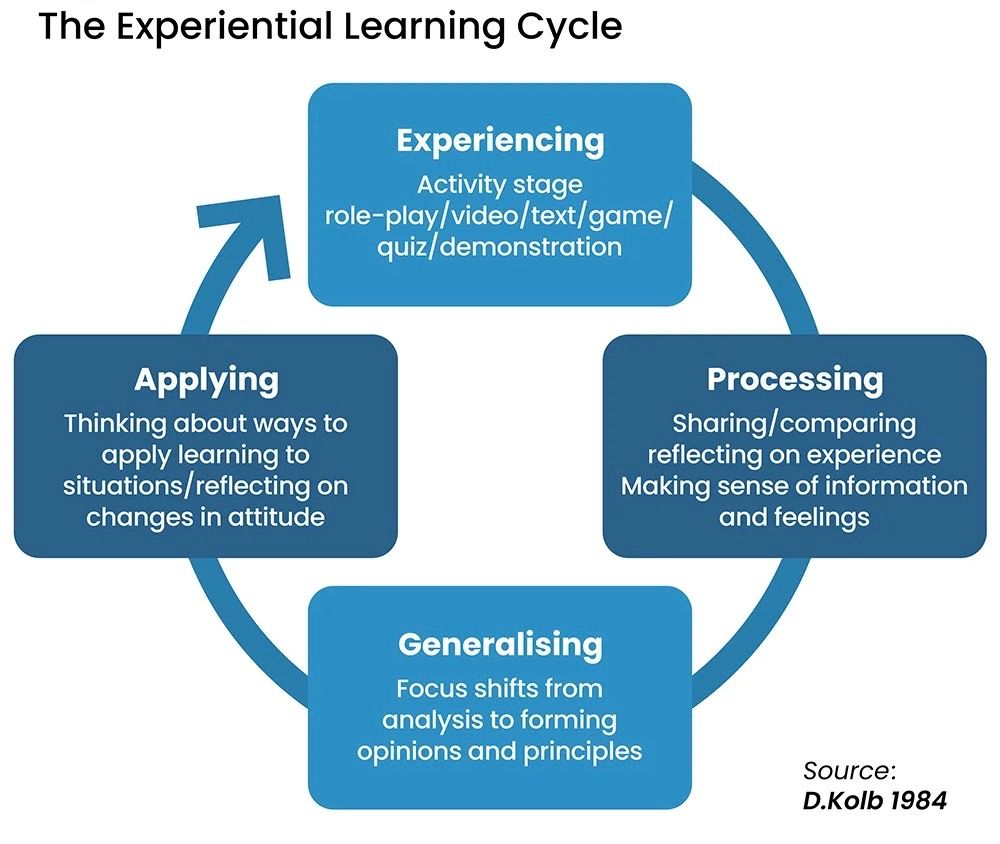
- Concrete Experience such as learning to ride a bike, speak a language, or play an instrument.
- Reflective Observation, or a learner thinking on the experiences they had, or observing others complete the task, during training courses.
- Abstract Conceptualisation, where learners then work on improving or developing action plans for their skills for a specific course of training.
- Active Experimentation by acting on knowledge acquired across the training course to complete tasks with greater efficacy.
According to research citing the Cohen scale, which measures the effect of a teaching method on learner retention, students averaged between 0.50 and 0.79 on the scale, revealing a moderate impact on learner retention and efficacy.
This is equal to making huge impact on achieving targeted goals faster and with more accuracy. Following such theoretical practices is the backbone of tackling the upskilling challenges across the global workforce.
Employees and remote workers require reliable, standardised and rapid kills solutions to meet enterprise goals. The XR Association continues to document the utility of experiential learning and extended reality, namely as workforces and companies work to overcome the ongoing skills shortage crisis.
Extended Reality and Experiential Learning
Immersive firms truly shine in the field of experiential learning as they leverage the power of spatial computing to engage learners. For example, extended reality firms can allow designers to create holistic learning experiences and environments with bespoke, Gen AI user-generated content (UGC).
By doing so, instructors and developers can progress people across the entire experiential learning cycle, leading to more effective outcomes. For designers and content curators, it is vital to incorporate these training methodologies into their experiences to produce the highest quality results while, additionally, measuring success rates with learning management systems.
For example, it may become more relevant to hold a person’s full attention with virtual reality with a high-definition video, training instructions, or role-playing scenarios. Afterwards, instructors can move to a VR/MR space, where they can trial a digital twin of a working environment to assess reaction times and choices.
Finally, a curricula designer can then switch the headset to AR, where learners can practice in real-world environments with digital content overlayed on devices, recognised objects etc. with spatially anchored information.
This inevitably leads to progressive learning throughout the entire learner journey, effectively producing employees that are focused on their objectives.
ARuVR and XR Experiential Learning
XR training companies like ARuVR, Oberon Technologies, Rock Paper Reality, Meta, Lenovo, and many others are putting their hats in the ring by developing hardware, software and solutions capable of bringing the full benefits of experiential learning to all.
This has accomplished enormous, measurable successes across many industry verticals. Additionally, clarity in curricula design, training pedagogy and progressive skill-building has led ARuVR to receive G-Cloud 13, Crown Commercial Services and LPI accreditation for their technologies. This has led to standardised solutions trusted by the global immersive learning industry.
As the XR industry evolves, hardware such as the Meta Quest Pro, Apple Vision Pro, HTC VIVE XR Elite and Lenovo VRX etc. will unlock greater potential for theory to come into practice, for the benefit of society.
Frank Furnari 
CEO & Founder at ARuVR
Demond Cureton 
Senior Reporter at XR Today



)
)


)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)